In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, artificial intelligence has transformed from a futuristic concept to an everyday tool. At the heart of effectively using AI systems like ChatGPT, Claude, and other large language models lies a crucial skill: prompt engineering. This comprehensive guide will take you through the fundamentals, advanced techniques, and practical applications of prompt engineering, empowering you to communicate with AI more effectively and unlock its full potential.
Prompt engineering is the art and science of crafting inputs that effectively communicate your intentions to AI systems. Think of it as learning a new language—the language of speaking to artificial intelligence. When you master prompt engineering, you’re essentially learning how to communicate your needs in a way that AI models can understand and respond to optimally.
The significance of prompt engineering cannot be overstated. A well-crafted prompt can be the difference between receiving a generic, unhelpful response and obtaining precisely the information or assistance you need. As AI becomes increasingly integrated into our professional and personal lives, the ability to communicate effectively with these systems becomes not just valuable but essential.
Get Started!
Why Prompt Engineering Matters
AI models like large language models (LLMs) are trained on vast amounts of text data, learning patterns and relationships between words and concepts. However, they lack human intuition and context awareness. When you provide a vague or ambiguous prompt, the AI must make assumptions about what you want—often leading to responses that miss the mark.
Effective prompt engineering bridges this gap. By being explicit, specific, and structured in your requests, you provide the AI with the necessary context and direction to generate useful outputs. This skill becomes particularly important when:
- You need precise information or specific formatting
- You’re working with complex or technical topics
- You’re trying to solve multi-step problems
- You need creative content that matches your vision
- You’re using AI for professional or specialized tasks
The Evolution of Human-AI Interaction
Prompt engineering represents a significant shift in how we interact with technology. Traditional software requires users to learn its interface and commands—you adapt to the technology. With AI, the dynamic is different: through prompt engineering, you’re teaching the technology to adapt to your needs.
This shift creates a more natural and flexible interaction paradigm, but it also places greater responsibility on the user to communicate effectively. As one industry expert noted, “The quality of AI outputs is directly proportional to the quality of human inputs.” By mastering prompt engineering, you’re positioning yourself at the forefront of this new way of interacting with technology.
The Core Principles of Effective Prompting
Before diving into specific techniques, let’s establish the fundamental principles that underpin successful prompt engineering:
Clarity and Specificity: The Foundation of Good Prompts
AI systems take your words literally. They don’t have the human ability to read between the lines or infer unstated intentions. This makes clarity and specificity paramount.
Consider the difference between these two prompts:
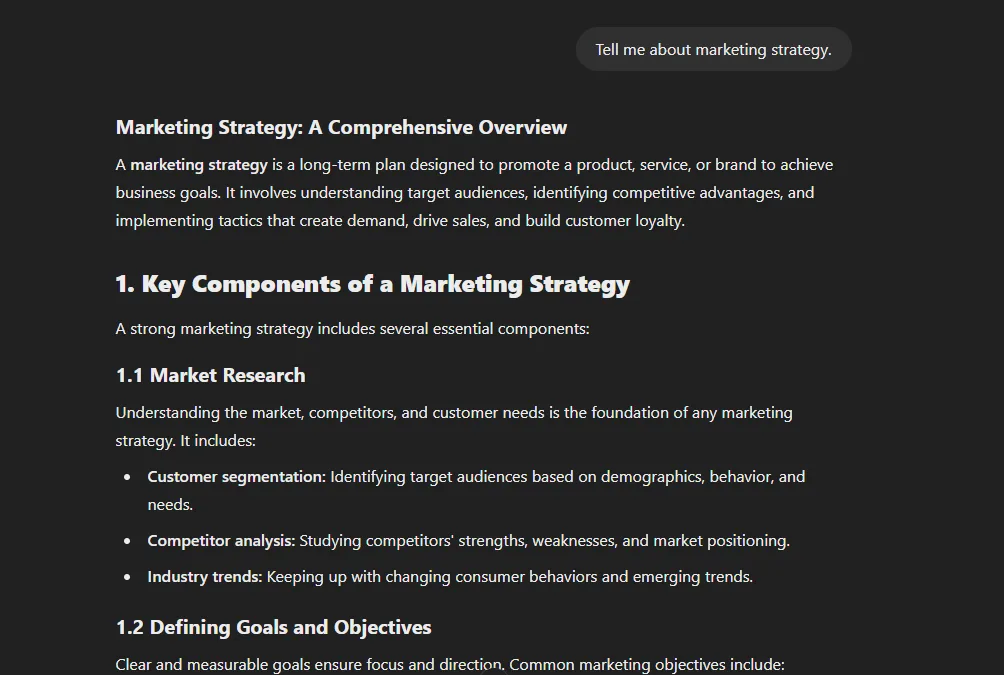
“Tell me about marketing strategy.”
Versus:
“Explain the key components of a digital marketing strategy for a small e-commerce business selling handmade jewelry, focusing on social media and email marketing tactics.”

Digital Marketing Strategy for a Small E-Commerce Business Selling Handmade Jewelry
A small e-commerce business selling handmade jewelry needs a well-planned digital marketing strategy to attract customers, build brand loyalty, and drive sales. This strategy will focus on social media marketing and email marketing as primary channels.
1. Social Media Marketing Strategy
Social media is a powerful tool for an e-commerce business, helping to build brand awareness, engage with customers, and increase sales. Here’s how to optimize social media marketing for a handmade jewelry business:
1.1 Choosing the Right Platforms
Instagram – Best for visually appealing products, featuring high-quality images, Instagram Reels, and Stories.
Facebook – Great for running targeted ads, engaging with customers through a business page, and selling directly through Facebook Shops.
Pinterest – Ideal for inspiration-seeking users, showcasing jewelry designs, and driving traffic to the website.
TikTok – Perfect for showcasing behind-the-scenes content, customer testimonials, and viral trends.
1.2 Content Strategy
Product Showcase – High-quality images and videos displaying jewelry from different angles and in natural settings.
Behind-the-Scenes – Short clips of the jewelry-making process, showing craftsmanship and authenticity.
User-Generated Content – Encourage customers to post photos wearing the jewelry and share testimonials.
Educational Posts – Explain jewelry care tips, styling guides, and gemstone meanings.
Storytelling & Brand Story – Share your journey as a jewelry maker, highlighting unique selling points.
Giveaways & Contests – Boost engagement and reach by offering free jewelry in exchange for follows, likes, or user-generated content.
Limited-Time Offers & Flash Sales – Create urgency with discounts or exclusive product drops.
1.3 Posting Frequency & Scheduling
Instagram & Facebook: Post 4-5 times per week, with a mix of photos, carousels, Reels, and Stories.
Pinterest: Upload 10-20 pins per week, including repins.
TikTok: Post 3-4 short videos per week, using trends and popular sounds.
1.4 Hashtags & SEO Optimization
Use relevant hashtags like #HandmadeJewelry, #JewelryLover, #MinimalJewelry, #BohoAccessories to improve discoverability.
Optimize post captions with keywords to appear in searches.
1.5 Influencer & Collaboration Strategy
Partner with micro-influencers (5K-50K followers) who align with your brand and have high engagement rates.
Offer affiliate programs where influencers earn a commission on sales.
Collaborate with other small businesses (e.g., handmade fashion brands) for cross-promotions.
1.6 Paid Advertising
Instagram & Facebook Ads: Run carousel ads, story ads, and retargeting ads targeting people who visited the website.
Pinterest Ads: Promote best-performing pins to increase reach.
TikTok Ads: Use short-form video ads to drive traffic to your store.
2. Email Marketing Strategy
Email marketing is crucial for nurturing leads, retaining customers, and increasing repeat sales. Here’s how to create an effective email marketing strategy:
2.1 Building an Email List
Website Pop-Ups: Offer a 10-15% discount for first-time subscribers.
Exit-Intent Pop-Ups: Capture emails before users leave the website with special offers.
Lead Magnets: Provide free resources like a "Jewelry Care Guide" in exchange for email sign-ups.
Social Media Campaigns: Promote exclusive discounts for newsletter subscribers.
2.2 Types of Emails to Send
Welcome Series (Automated)
Email 1: Introduction & Brand Story (Sent immediately)
Email 2: Best-Sellers & Social Proof (Sent after 2 days)
Email 3: Limited-Time Discount (Sent after 5 days)
Product Launch & Special Offers
Announce new jewelry collections and exclusive discounts.
Abandoned Cart Recovery
Email 1: Reminder with product images (Sent within 1 hour)
Email 2: Offer a 5-10% discount (Sent after 24 hours)
Email 3: Highlight urgency (Sent after 48 hours)
Seasonal & Holiday Campaigns
Promote jewelry as gift ideas for occasions like Valentine’s Day, Mother’s Day, and Christmas.
Loyalty & VIP Programs
Reward repeat customers with exclusive discounts, early access to new collections, or referral bonuses.
Post-Purchase Follow-Ups
Ask for reviews and user-generated content.
Provide a Jewelry Care Guide to enhance customer experience.
2.3 Personalization & Segmentation
Segment email lists based on:
Purchase history (Frequent buyers vs. new customers)
Browsing behavior (Interested in rings vs. earrings)
Engagement levels (Highly active subscribers vs. inactive users)
Use personalized subject lines and product recommendations based on past purchases.
2.4 Email Frequency
Newsletter: Send 1-2 emails per week with valuable content (not just promotions).
Promotions: Send during major sales events, new product drops, or holidays.
Cart Abandonment & Follow-Ups: Automated based on user actions.
3. Measuring & Optimizing Performance
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) helps refine strategies over time.
3.1 Social Media Metrics
Engagement Rate: Likes, comments, shares, saves.
Reach & Impressions: How many people saw the content.
Follower Growth: Monthly increase in audience size.
Click-Through Rate (CTR): How many users clicked on the website link.
Conversion Rate: Percentage of visitors who made a purchase.
3.2 Email Marketing Metrics
Open Rate: Percentage of recipients who opened the email.
Click-Through Rate (CTR): Percentage of recipients who clicked a link.
Conversion Rate: Percentage of subscribers who made a purchase.
Unsubscribe Rate: How many users opted out after receiving emails.
Conclusion
By combining an effective social media marketing strategy with a well-structured email marketing campaign, a small e-commerce business selling handmade jewelry can increase brand visibility, attract new customers, and drive repeat sales. The key is to focus on high-quality visuals, storytelling, customer engagement, and data-driven optimizations.The first prompt is vague and could lead to a generic overview of marketing. The second prompt provides clear parameters—the type of business, the size, the product category, and the specific marketing channels of interest. This level of detail guides the AI toward generating a much more relevant and useful response.
Context Provides Meaning
Context is what transforms isolated information into meaningful insights. When crafting prompts, providing relevant context helps the AI understand the broader picture and tailor its response accordingly.
Effective context might include:
- Your objective or goal
- Background information about the topic
- Your knowledge level on the subject
- How you plan to use the information
- Any constraints or requirements
For example, adding “I’m a beginner with no technical background” signals to the AI that it should avoid jargon and provide foundational explanations. Conversely, stating “I have advanced knowledge in this field” indicates that more sophisticated content would be appropriate.
Setting the Tone and Style
AI can adapt its writing style and tone based on your directions. This flexibility allows you to obtain content that matches your needs, whether for a professional email, a creative story, or an academic paper.
You can specify elements like:
- Formality level (casual, professional, academic)
- Emotional tone (enthusiastic, neutral, serious)
- Writing style (conversational, technical, narrative)
- Voice (active vs. passive)

For instance, requesting “Explain quantum computing in an enthusiastic, conversational tone as if speaking to a curious teenager” will yield a fundamentally different response than “Provide a technical explanation of quantum computing suitable for a graduate-level physics course.”
The Power of Structure and Format
Structure and format instructions give you control over how information is presented. AI can organize content in various ways, from essays to dialogues to step-by-step guides.
Being explicit about your desired format improves the usability of the response. This might include:
- Specifying the length (number of paragraphs, word count)
- Requesting particular sections or headings
- Asking for a specific narrative structure
- Indicating if you want definitions, examples, or analogies included
By combining these core principles—clarity, context, tone, and structure—you create a foundation for effective prompts that consistently yield high-quality outputs from AI systems.
From Beginner to Advanced: Prompt Engineering Techniques
Let’s explore specific techniques you can apply to enhance your prompt engineering skills, starting with fundamentals and progressing to more sophisticated approaches.
Using Delimiters for Clarity
Delimiters are markers that separate different parts of your prompt, helping the AI distinguish between instructions, data, examples, and other elements. Common delimiters include:
- Triple backticks (“`) for code or text blocks
- XML-style tags (<example>…</example>)
- Distinctive markers like ### or —
Delimiters are particularly valuable when your prompt includes multiple components.
For example:
Analyze the customer feedback between triple quotes and identify the main complaints.
“””
The app keeps crashing when I try to upload photos.
I’ve been a loyal customer for years, but this latest update is terrible.
The new interface is confusing, and customer support hasn’t responded to my email from three days ago.
“””
The triple quotes clearly separate the instruction from the content to be analyzed, preventing confusion.
Advantages of Using XML-style Tags:
Works well when structuring multiple types of input (e.g., <instruction>, <feedback>, <metadata>).
Helps maintain clear organization in complex prompts.
Allows for better formatting when AI processes structured data.
<analysis>
<complaints>
<crash>App crashes when uploading photos</crash>
<update>Latest update is perceived as terrible</update>
<interface>Confusing new interface</interface>
<support>No response from customer support in three days</support>
</complaints>
</analysis>
Role-Based Prompting
Role-based prompting involves asking the AI to adopt a specific perspective or expertise when generating a response. This technique leverages the AI’s ability to simulate different viewpoints and knowledge bases.
For example, instead of asking “How can I improve my website’s SEO?”, you might prompt:
“As an experienced SEO consultant with 15 years in the industry, what would be your top three recommendations for improving the search engine visibility of a small business blog in the health and wellness niche?”

This approach encourages more specialized and nuanced responses, as the AI attempts to emulate the expertise and perspective of the specified role.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
For complex problems requiring logical reasoning, chain-of-thought prompting encourages the AI to break down its thinking process step by step. This technique improves accuracy and allows you to follow the AI’s reasoning.
You can implement this by explicitly requesting a step-by-step approach:
“Solve this probability problem step by step, explaining your reasoning at each stage: In a class of 30 students, what is the probability that at least two students share the same birthday?”
Research has shown that prompting the AI to “think step by step” significantly improves performance on reasoning tasks, as it mimics the deliberate thinking process humans use when solving complex problems.
Few-Shot Learning Through Examples
Few-shot learning involves providing examples of the type of response you want, allowing the AI to pattern-match and produce similar outputs. This technique is particularly effective when:
- You need a specific format or style
- You’re asking for creative content with particular characteristics
- You want consistent responses across multiple queries
For instance, if you need product descriptions in a specific style:
“Write a product description for a wireless bluetooth headphone in the same style as these examples:
Example 1: Our moisture-wicking yoga pants blend comfort and performance. The four-way stretch fabric moves with you during even the most challenging poses, while the high waistband provides support and confidence. Available in three stunning earth-tone colors.
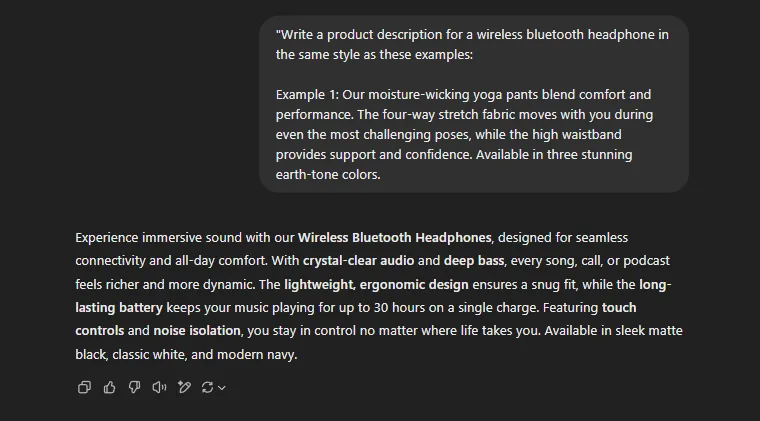
Example 2: This minimalist ceramic mug transforms your morning ritual. Hand-thrown by artisan craftspeople, each piece features subtle variations in texture. The ergonomic handle and heat-retention design keep your favorite brew at the perfect temperature.”

The AI will analyze the pattern, style, and structure of your examples and apply them to the new product.
Self-Correction and Refinement Techniques
Rather than starting from scratch when a response isn’t quite right, you can guide the AI to refine its own output. This iterative approach often leads to higher quality results.
There are several ways to implement this:
- Asking the AI to critique its response: “Review your answer above and identify any weaknesses or limitations in your explanation.”
- Suggesting specific improvements: “Your explanation of photosynthesis was good, but could you add more detail about the light-dependent reactions?”
- Requesting an alternative approach: “That approach works, but can you suggest a different method that might be more efficient?”
This collaborative refinement process mimics human learning and often produces more thoughtful and comprehensive responses.
Advanced Prompt Engineering Strategies for Complex Tasks
As you become more comfortable with basic techniques, you can implement more sophisticated strategies for handling complex tasks and specialized needs.
System Prompts and Guardrails
System prompts (sometimes called system messages) set the foundational behavior and constraints for the AI. While not always directly accessible in consumer interfaces, understanding this concept is valuable for advanced users.
System prompts essentially establish:
- The AI’s role or persona
- Global constraints and rules
- Output format preferences
- Ethical boundaries
In professional settings or when using AI APIs, system prompts can create guardrails that ensure consistent, appropriate responses. For example, a customer service AI might have a system prompt that requires it to always be polite, never speculate about product features not yet announced, and always offer to connect the customer with a human representative if needed.
These guardrails establish boundaries that remain in effect throughout the entire conversation, reducing the need to repeat instructions and ensuring consistent quality.
Multi-Stage Prompting for Complex Projects
Complex projects often benefit from breaking the task into discrete stages, allowing the AI to focus on one aspect at a time. This approach mimics how humans tackle complicated projects.
For example, if you’re creating a comprehensive marketing plan, you might use a sequence of prompts:
Stage 1: “Analyze the target market for a new organic skin care line, focusing on demographics, psychographics, and buying behaviors.”
Stage 2: “Based on the market analysis above, develop positioning statements that would resonate with the identified customer segments.”
Stage 3: “Using the positioning from your previous response, outline a content marketing strategy with specific channel recommendations.”
Each stage builds on the previous one, creating a coherent progression that results in a more thorough and thoughtful final product.
Integration of External Knowledge
While AI models have extensive training data, they may lack specific or current information relevant to your needs. You can enhance responses by integrating external knowledge into your prompts.
This might include:
- Current statistics or data
- Specific documents or text
- Recent events or developments
- Specialized terminology or frameworks
For instance:
“Using the following quarterly sales data, analyze the trends and suggest strategies for improvement:
Q1: $1.2M
Q2: $1.5M
Q3: $1.3M
Q4: $1.8M
Our top-performing product categories were electronics and home goods, while apparel underperformed expectations by 15%.”

By providing this specific information, you ground the AI’s response in your actual data rather than generalizations.
Template-Based Approaches for Consistency
For recurring tasks, developing standardized prompt templates ensures consistent outputs and saves time. Templates are particularly valuable in professional settings where multiple team members might be interacting with AI systems.
A basic template might include:
- Context section (background information)
- Task definition (specific request)
- Format requirements
- Constraints or limitations
- Examples (if applicable)
Templates can be customized for different use cases—content creation, data analysis, customer communications, etc.—while maintaining a consistent structure that maximizes the AI’s effectiveness.
Domain-Specific Prompt Engineering
Different fields have unique requirements and considerations when it comes to prompt engineering. Let’s explore how prompt techniques can be tailored to specific domains.
Creative Content Generation
When using AI for creative writing, storytelling, or artistic content, prompts that establish clear parameters while allowing room for imagination work best.
Effective techniques include:
- Providing detailed sensory descriptions to set the scene
- Establishing character traits, motivations, and backgrounds
- Specifying the emotional impact you want the content to have
- Defining the genre conventions and style elements to include
For example:
“Write a short story set in a small coastal town during the off-season. The protagonist is a local bookstore owner who discovers an unusual manuscript left behind by a mysterious tourist. The story should have elements of magical realism and convey a sense of bittersweet nostalgia. The writing style should be lyrical and atmospheric, similar to authors like Erin Morgenstern or Neil Gaiman.”
Go to See Result of Prompt: CLICK
This prompt provides rich context and clear creative direction while leaving space for the AI to generate original content.
Business and Professional Communication
In business contexts, clarity, professionalism, and alignment with organizational objectives are paramount. Prompts should emphasize these elements.
Key considerations include:
- Specifying the business context and stakeholders involved
- Defining the communication objective (inform, persuade, request)
- Noting any relevant policies, values, or brand guidelines
- Indicating the level of formality and technical detail appropriate for the audience
For instance:
“Draft an internal email announcing our new flexible work policy to all employees. The policy allows team members to work remotely up to three days per week, starting next month. The tone should be positive and supportive, emphasizing that this change reflects our trust in employees and commitment to work-life balance. Include practical details about how to coordinate schedules with team managers and mention that a comprehensive guide will be shared next week.”

This prompt provides specific parameters that ensure the resulting communication will be relevant and appropriate.
Technical and Educational Content
When creating technical documentation, tutorials, or educational materials, prompts should emphasize accuracy, clarity, and appropriate scaffolding of concepts.
Effective approaches include:
- Specifying the expertise level of the intended audience
- Requesting definitions of key terms or concepts
- Asking for analogies or visualizations to illustrate complex ideas
- Requiring step-by-step explanations with clear transitions
For example:
“Explain how public key cryptography works to a computer science undergraduate. Start with the basic concept, then explain the mathematical principles in simplified terms. Include a real-world analogy to make the concept more intuitive, and conclude with common applications like SSL/TLS. Avoid overly technical jargon, but don’t oversimplify to the point of inaccuracy.”
This type of prompt ensures that technical content is accessible without sacrificing depth or accuracy.
Ethical Considerations in Prompt Engineering
As prompt engineering becomes more sophisticated, ethical considerations become increasingly important. Responsible use of AI requires awareness of potential pitfalls and best practices.
Avoiding Manipulation and Misuse
Prompt engineering skills can be used to attempt to manipulate AI systems into producing harmful, biased, or inappropriate content. This misuse—sometimes called “prompt hacking” or “jailbreaking”—raises serious ethical concerns.
Responsible prompt engineers should:
- Avoid techniques designed to circumvent safety mechanisms
- Not attempt to extract private or sensitive information
- Refrain from generating content that could cause harm
- Consider the potential impacts of the content they request
Instead, focus on techniques that enhance the quality, relevance, and accuracy of AI responses within appropriate ethical boundaries.
Mitigating Bias in Prompts and Responses
AI systems can reflect and sometimes amplify biases present in their training data. Your prompts can either mitigate or exacerbate these biases.
To craft more equitable prompts:
- Examine your assumptions and framing
- Use inclusive and neutral language
- Request diverse perspectives and examples
- Be cautious with stereotypes and generalizations
For example, when requesting content about leadership, avoid assuming leaders are of a particular gender or background. Instead, explicitly ask for diverse examples if representation is important.
Transparency and Attribution
When using AI-generated content, transparency about its origins is an emerging ethical standard. This is particularly important in professional, academic, and public contexts.
Best practices include:
- Disclosing when content is AI-generated or AI-assisted
- Maintaining human oversight and responsibility for the final output
- Not presenting AI-generated content as human expertise
- Properly citing sources when the AI references specific works
The Future of Prompt Engineering
As AI technology continues to evolve, prompt engineering will likely transform alongside it. Several trends are already emerging that point to the future of this discipline.
Multimodal Prompting
Newer AI systems can process and generate multiple types of media—text, images, audio, and eventually video. This capability is expanding the scope of prompt engineering beyond text.
Multimodal prompting involves crafting inputs that might include:
- Text descriptions alongside images
- Audio samples with textual instructions
- Sketches or diagrams with explanatory notes
These combined inputs create richer context for the AI, enabling more nuanced and creative outputs. As models become more sophisticated, the interplay between different types of inputs will open new possibilities for communication with AI systems.
Automated and Assisted Prompt Engineering
As prompt engineering grows in importance, tools are emerging to help users craft effective prompts without deep expertise. These range from prompt templates and libraries to AI systems that help optimize prompts.
Some systems now offer:
- Prompt suggestions based on your goal
- Analysis of prompt effectiveness
- Automated refinement of ineffective prompts
- Libraries of tested prompts for common use cases
This development democratizes access to effective AI use, allowing even beginners to benefit from advanced prompt engineering techniques.
Integration with Specialized Knowledge Systems
The next generation of AI systems will likely combine large language models with specialized knowledge bases and computational tools. This integration will change how we craft prompts.
Future prompting might involve:
- Directing the AI to consult specific databases
- Instructing it to use particular analytical tools
- Referencing proprietary documents or knowledge
- Combining natural language with more formal query languages
This evolution will require prompt engineers to understand not just how to communicate with the AI, but also how to leverage its connections to other systems and information sources.
Prompt engineering represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with technology. Rather than learning complex interfaces or programming languages, we’re developing a new communicative skill—speaking clearly and effectively to artificial intelligence.
The principles and techniques covered in this guide provide a foundation for this emerging skill. From basic clarity and context to sophisticated multi-stage approaches, effective prompt engineering allows you to harness the full potential of AI systems.
As you practice and refine these techniques, remember that prompt engineering is both an art and a science. It combines technical understanding with creativity, precision with adaptability. The most effective prompt engineers develop an intuitive feel for how to communicate with AI while applying structured approaches to complex problems.
In a world where AI is becoming increasingly integrated into our work and lives, the ability to craft effective prompts is more than a technical skill—it’s a form of literacy for the AI age. By mastering this new language of human-AI communication, you position yourself to leverage these powerful tools more effectively than ever before, turning artificial intelligence into a true collaborator in your creative and professional endeavors.
What is prompt engineering, and why is it important?
Prompt engineering is the process of crafting precise and structured inputs to guide AI models like ChatGPT and Claude in generating relevant and high-quality responses. It is important because a well-structured prompt improves the accuracy and usefulness of AI-generated content, reducing ambiguity and increasing efficiency in tasks such as research, content creation, and problem-solving.
How can I write better AI prompts to get accurate responses?
To write better AI prompts, focus on clarity and specificity. Avoid vague or broad instructions, and instead provide detailed context to guide the AI. Defining the desired format, such as step-by-step explanations or structured responses, can help generate more precise results. Using examples to demonstrate the expected style or structure also improves accuracy. Additionally, specifying the tone, whether formal, casual, or technical, ensures that the output matches your needs.
What are the most effective techniques for prompt engineering?
Several techniques enhance AI-generated responses. Role-based prompting involves asking the AI to respond from a specific perspective, such as an expert in a given field. Chain-of-thought prompting encourages step-by-step reasoning for more logical responses. Few-shot learning provides examples within the prompt to guide AI outputs. Delimiters, such as triple quotes or XML tags, help separate sections of complex queries. Iterative refinement allows users to request improvements or clarifications from the AI to enhance its response.
How does prompt engineering improve AI-generated content for businesses?
Businesses benefit from prompt engineering by ensuring AI-generated content aligns with professional needs. In marketing and SEO, precise prompts help produce keyword-rich content. Customer support teams use structured AI responses for automated chats and emails. Data analysts apply AI prompts to summarize and generate insights from large datasets. Copywriting prompts can refine messaging for branding, email marketing, and advertising. By fine-tuning prompts, businesses can optimize AI outputs for their industry-specific requirements.
What are the future trends in prompt engineering?
The future of prompt engineering includes multimodal prompting, where AI integrates text, images, and audio for more interactive responses. Automated prompt refinement tools will assist users in crafting better inputs for more effective AI outputs. AI systems will increasingly connect with external knowledge bases, providing more accurate and up-to-date insights. Ethical considerations will play a larger role in prompt design, focusing on reducing bias and misinformation. Additionally, specialized AI models tailored for domains such as law, medicine, and cybersecurity will require advanced prompt engineering techniques to maximize their effectiveness.